Cryptocurrencies are not as new as they were a few years ago, but they surely retain the vibe of a new and complex concept for regulators around the world. Therefore, the laws and rules regarding these assets are still a work in progress everywhere, with some already here, some in the future, and some evolving along the way.
Since the start of the year, several jurisdictions have weighed in on the matter, changing the rules for many crypto users and businesses within their jurisdictions. It is always important to stay abreast of these developments, as they could directly affect us and our crypto funds. Next, let’s check out some noteworthy regulatory updates for the crypto industry worldwide in 2024 – so far.
Stablecoins and MiCA
The Regulatory Framework for Crypto-Asset Markets (MiCA) is not really new, having been proposed in 2020 and approved in 2023 for all European Union member states. However, this year is fundamental for its life cycle, being the implementation phase and entry into application from December 2024.
This regulation serves as a comprehensive guide for crypto asset service providers (CASPs) in the EU, aiming to strike a balance between encouraging innovation and protecting investors. Licensed financial entities must inform their national authorities about their crypto activities, while non-licensed entities are subject to a rigorous authorization process. MiCA also ensures that PSAPs effectively manage customer complaints by requiring clear, accessible and annually reviewed procedures, adequate resources and qualified staff to address issues quickly and fairly.
Needless to say, PSAPs – by definition – are centralized entities, even if they operate with decentralized cryptocurrencies or crypto platforms.
A critical point of the law is of course stablecoins and has caused concern among major providers, namely Tether (USDT) and USD Coin (USDC). **Under MiCA, issuers of stablecoins not linked to European currencies must stop issuing if daily transactions exceed 200 million euros, in order to prevent private entities from encroaching on the role of the euro . USDT and USDC, for example, are well above this daily limit. \ 

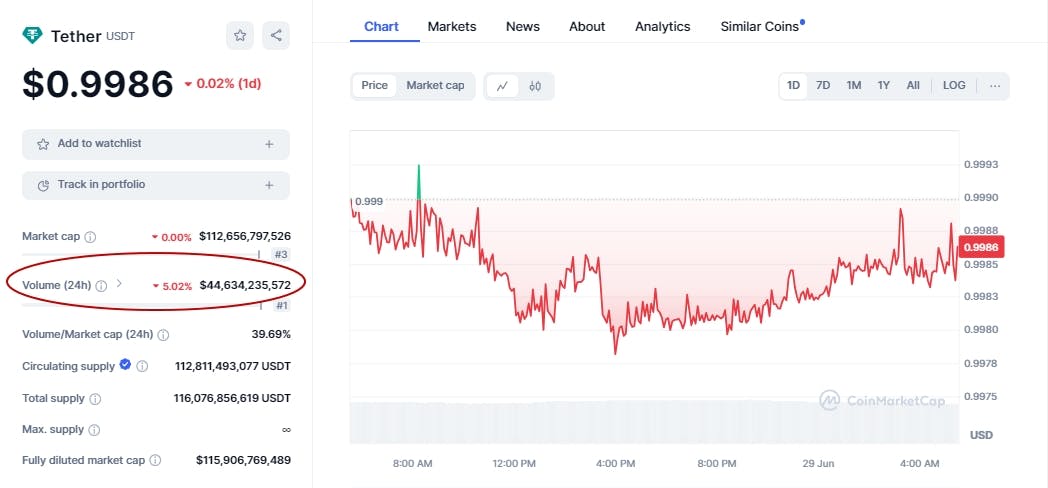
Additionally, even though they are linked to European currencies, they must comply with strict requirements and obtain an appropriate license to operate. Since June 2024,only Circle (USDC issuer) has acquired an Electronic Money Institution (EMI) license to continue working in the EU, while Tether Limited has not even tried it yet.
As a result, several cryptocurrency exchanges have started removing this asset from their EU client list, while Tether waiting for them to use it as a transactional gateway and not to allow direct exchanges with fiat. The specific MiCA rules for stablecoins began to take effect on June 30, 2024.
Against a CBDC USD and surveillance
Central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) can be a touchy subject for many people. Some of them (not even all) are, technically, cryptocurrencies in the sense that they are built with distributed ledger technology (DLT) and available for transacting worldwide. However, these are also coins entirely controlled by governments, and surveillance and censorship issues around them appeared more than once.
According to the Atlantic Council“134 countries and monetary unions, representing 98% of global GDP, are exploring a CBDC,” but most of them are in the research or pilot phase, and only three have successfully launched one through May 2024. 17 others are inactive, and at least two projects have been canceled. The United States joined the third bill canceled this year because the House of Representatives passed a bill prohibiting the Federal Reserve from issuing a USD CBDC. This would make the United States the first country to outright ban its own (potential) CBDC due to oversight concerns.


 In the same line against surveillance, the Worldcoin cryptography project is raising some fears around the world. Created by OpenAI founder Sam Altman, this company aims to create a unique digital identity by scanning people’s irises in exchange for a digital ID and some coins, supposedly to address identity verification in online in a world increasingly plagued by scams and AI identity theft. However, privacy experts are concerned on the collection and protection of biometric data, fearing misuse or unauthorized access.
In the same line against surveillance, the Worldcoin cryptography project is raising some fears around the world. Created by OpenAI founder Sam Altman, this company aims to create a unique digital identity by scanning people’s irises in exchange for a digital ID and some coins, supposedly to address identity verification in online in a world increasingly plagued by scams and AI identity theft. However, privacy experts are concerned on the collection and protection of biometric data, fearing misuse or unauthorized access.
Deceptive practices and data breaches have been reported, raising further questions about the security and ethical implications of the project. This is why it was questioned by regulators in more than ten countries and directly banned in Kenya, Portugal, Spain, Hong KongAnd probably Italy.
FIT21 and self-care in the United States
Aside from banning CBDCs, US regulators have been very busy this year. Probably one of the most important developments regarding cryptocurrencies was the Financial Innovation and Technology for the 21st Century Act (FIT21). This bill establishes a clearer regulatory framework for digital assets and gives the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) authority over decentralized digital assets. and the authority of the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) over centralized securities.
In other words, the CFTC would manage digital commodities (most cryptocurrencies), while the SEC would only supervise those considered securities. New and clear definitions would be put in place so that everyone in the industry knows what rules will be followed. FIT21 has been approved by the House of Representatives in May. The next steps for the bill to become law include passing it in the Senate, where it will receive further review, and then it must be signed by the president. The Biden administration has expressed opposition to the bill but has not threatened to veto it.
On the other hand, serious concerns about self-custodial wallets are persistent enough to several providers leave the country and its citizens. Afive, Phoenix and Wasabi withdrew from the United States, while the Department of Justice (DOJ) accused The founders of Samourai Wallet laundered money because of this software, just as they had previously accused the founders of Tornado Cash. Probably in reaction to this situation, the states of Oklahoma and Louisiana passed their own bills to protect the custodial rights of cryptocurrencies in their jurisdictions.
AML/KYC and new licenses
In 2021, as evidenced by a crypto regulation reportMost countries around the world already applied AML/KYC rules and procedures for cryptocurrency trading. Their number has only increased over the years and, sometimes, new related regulations have been added to the first ones. This can come down to correctly identifying customers of all crypto companies, and crypto users being forced to share their identity and documents when trading against fiat currencies.



Additionally, stricter requirements and licenses have emerged for cryptocurrency service providers. This is the case in Türkiye, where their Parliament approved the bill on Amendments to the Capital Markets Act in June 2024. This framework now requires crypto asset service providers to obtain authorization from the Capital Markets Board (SPK) for their establishment and operation, with technological criteria set by TÜBITAK (Scientific and Technological Research Council of Türkiye). It introduces definitions for crypto assets and service providers, requires independent financial audits and imposes strict penalties for unlicensed operations.
Other countries, for their part, have implemented or adjusted their own AML regulations for cryptocurrencies this year. Among them, we can count Singapore, Argentina, Kenya, Taiwan, India, Costa Ricaand even the European Union. In the last casethey are aiming for stricter measures, where crypto asset service providers will have to apply the same AML rules as banks for transactions above €1,000. At the very least, they do not explicitly impose these rules on self-custody wallet providers.
Crypto bans come and go
In September 2023, according to Atlantic Councilthere were at least 9 countries with a blanket ban on cryptocurrencies. One of them was Bolivia, and there’s actually some good news about that. In June 2024, the Central Bank of Bolivia (BCB) lifted its 4-year ban on cryptocurrency transactions, allowing financial entities to engage in cryptocurrency under new regulations.



This decisioncarried out in collaboration with the Financial System Supervisory Authority (ASFI) and the Financial Investigation Unit (UIF), follows the recommendation of the Latin American Financial Action Task Force (GAFILAT) to regulate financial services providers virtual assets in the country. The BCB aims to modernize the country’s payments system, improve financial infrastructure and promote digital financial inclusion.
On the other hand, the Central Bank of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) discussed issuing regulations on payment token services aimed at allowing stablecoins, requiring these tokens to be backed by UAE dirhams United Arab Emirates and are not linked to other currencies. For the crypto lawyer Irina Heaverthis could involve a practical ban on crypto payments inside the country. The results of this discussion and subsequent comments, however, remain to be seen.
Obyte as a safe place
It can be said that Ooctetbuilt on a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) system, positions itself as a robust platform resistant to surveillance, seizure of funds and censorship attempts. Unlike blockchain structures, Obyte’s miner-free DAG architecture allows for fully decentralized data storage and transaction validation, making it inherently resistant to centralized control.


This setup ensures that no entity can disapprove, seize, or censor transactions, thereby preserving user autonomy and providing privacy features. The platform’s emphasis on user control is further enhanced by its use of human-readable formats. smart contracts that run autonomously without the need for intermediaries or coding, reducing vulnerabilities to censorship efforts.
By leveraging its DAG technology, Obyte strengthens decentralization and autonomy, making it a potentially safer ecosystem for users concerned about privacy and security. This combination of features positions the ecosystem as a promising solution for those looking for a crypto platform that prioritizes user control and resilience against external interference.
Featured vector image by Freepik